Tissue Segmentation in OmnibusX
Just as cell type labels are fundamental to single-cell data analysis, tissue annotation is equally crucial for understanding spatial organization and biological context. In spatial transcriptomics, identifying tissue structures helps researchers interpret gene expression patterns, uncover spatially restricted cell states, and study disease-associated microenvironments with far greater clarity.
To support this essential analytical step, OmnibusX now integrates a dedicated tissue segmentation module directly into the desktop application. This feature brings structure-level understanding to your spatial datasets, without requiring additional tools, cloud resources, or complex model development.
Applicability across many tissue types
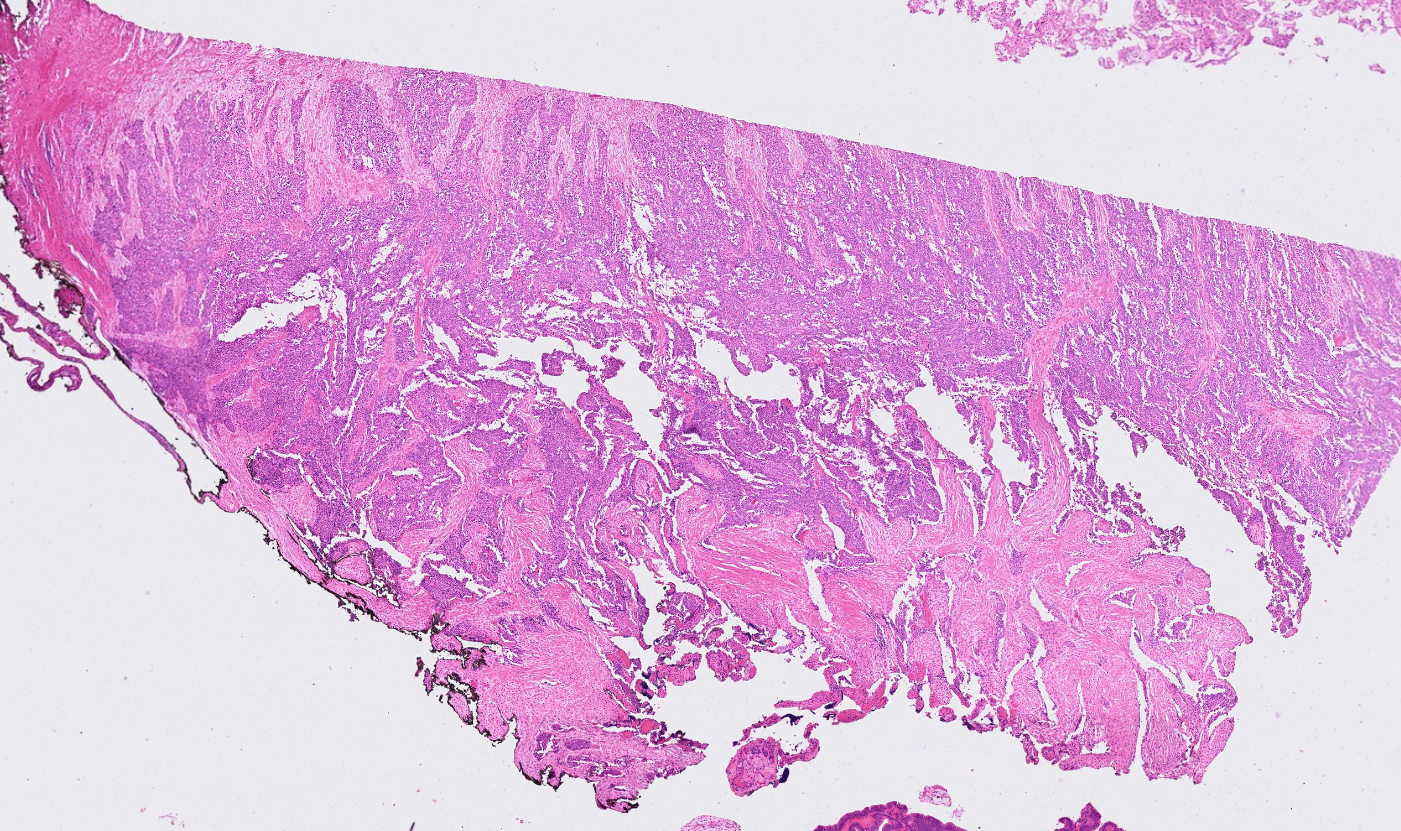
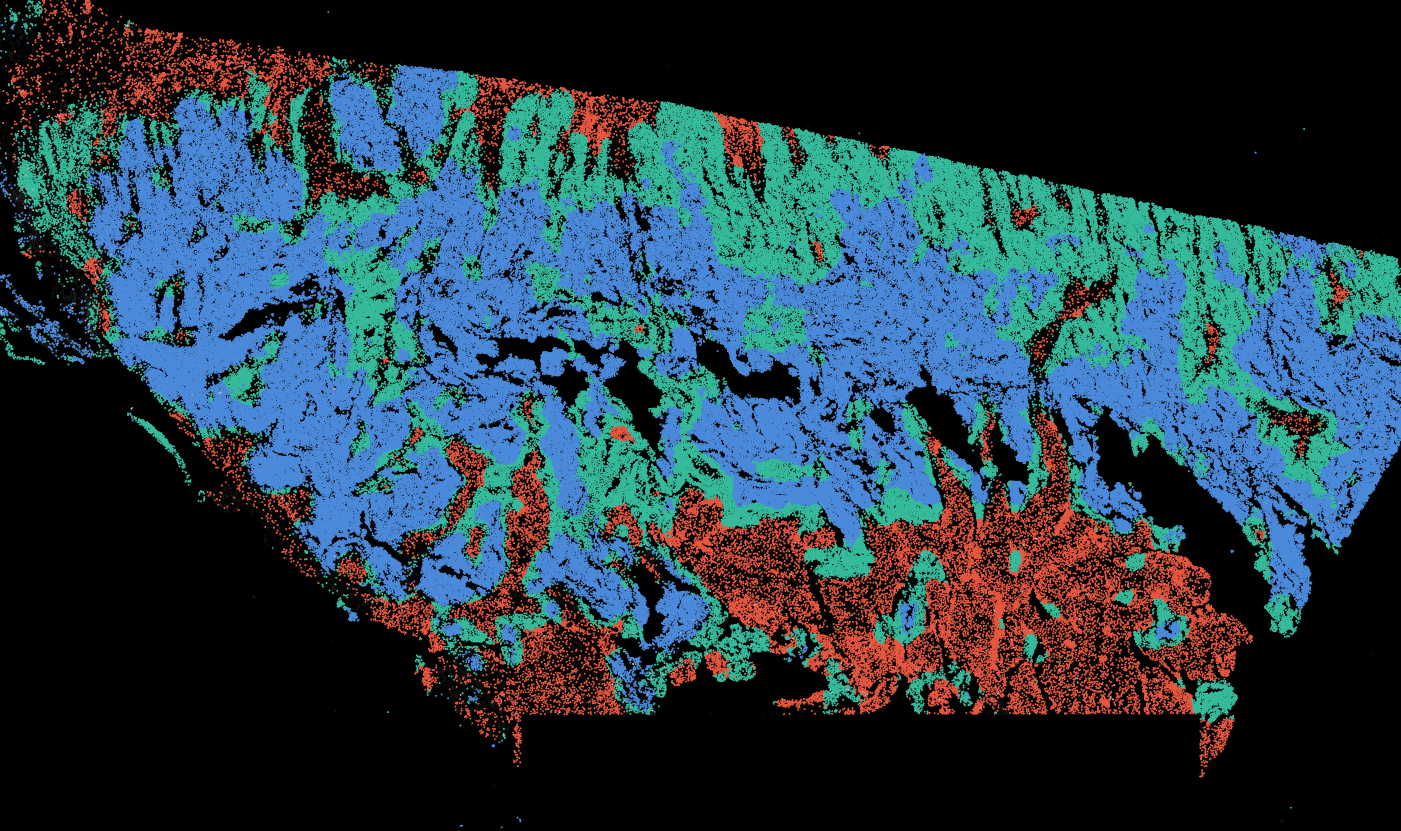
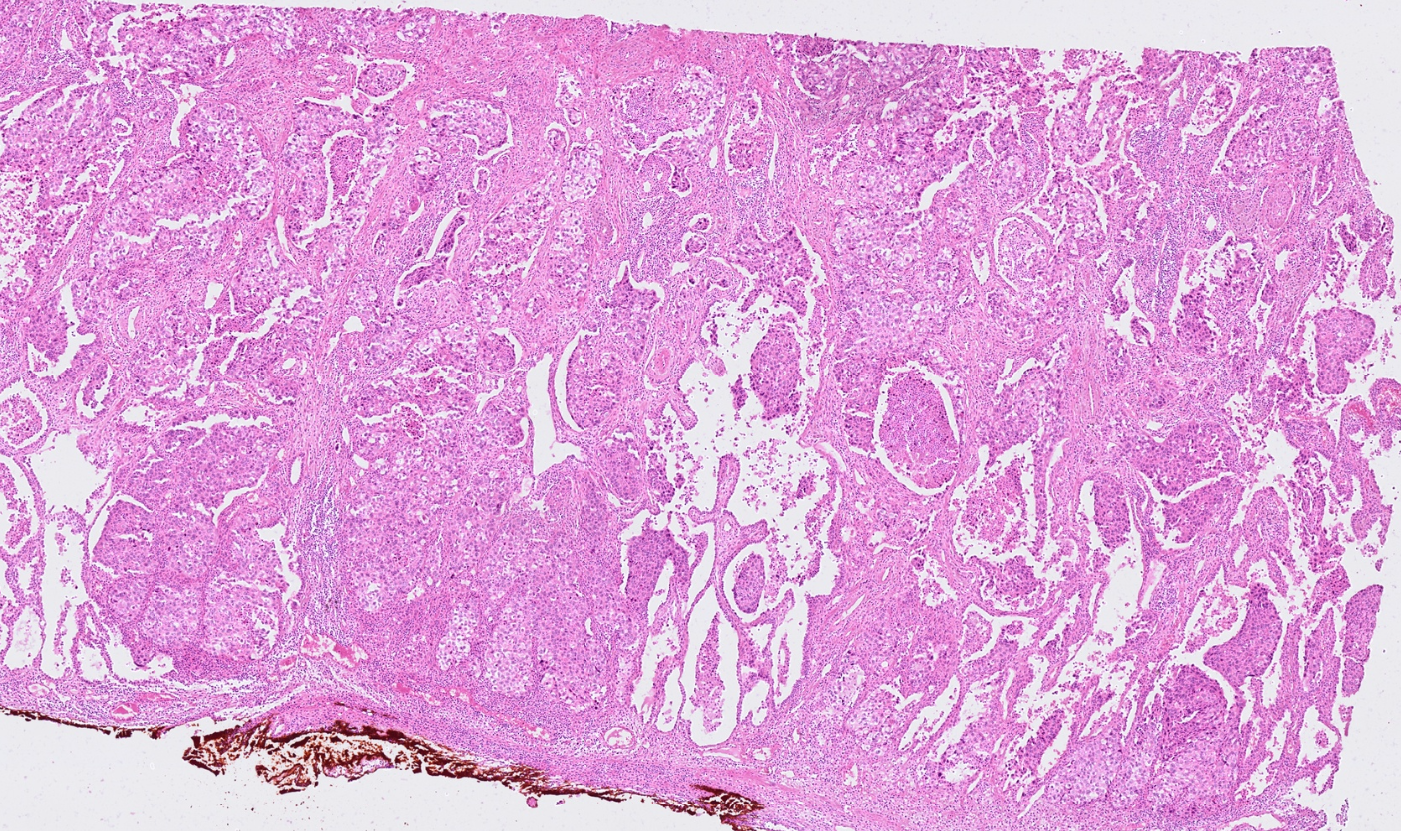
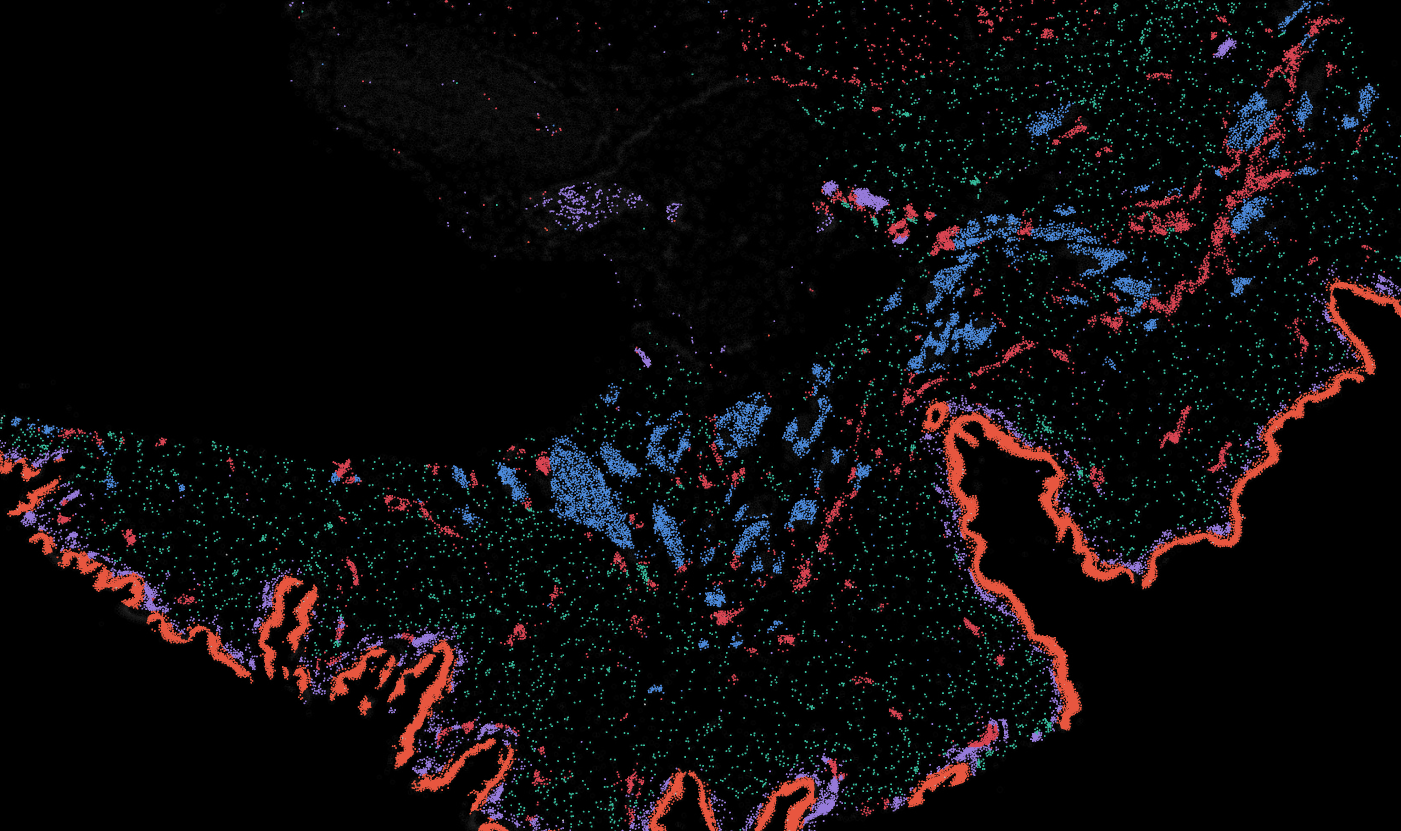
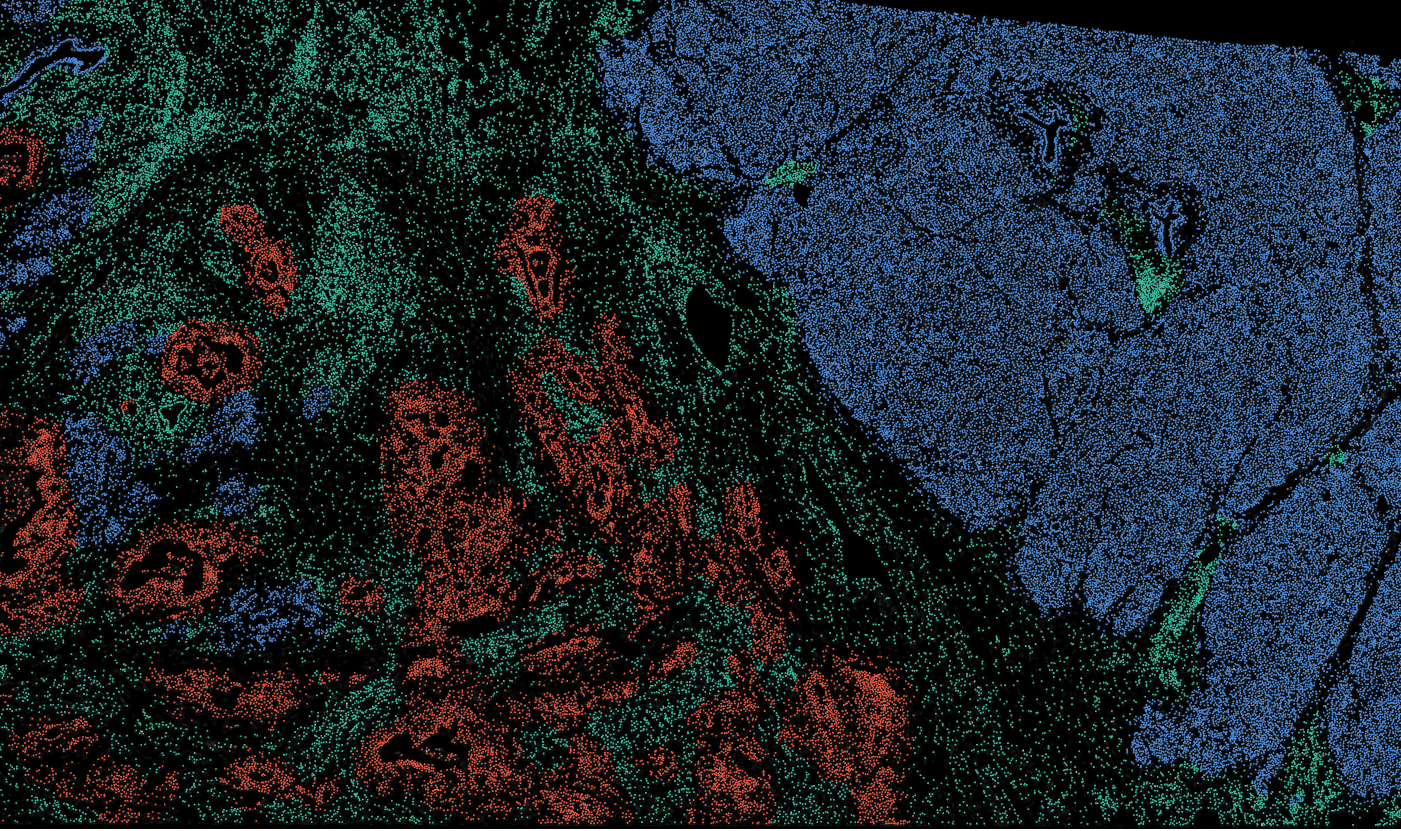
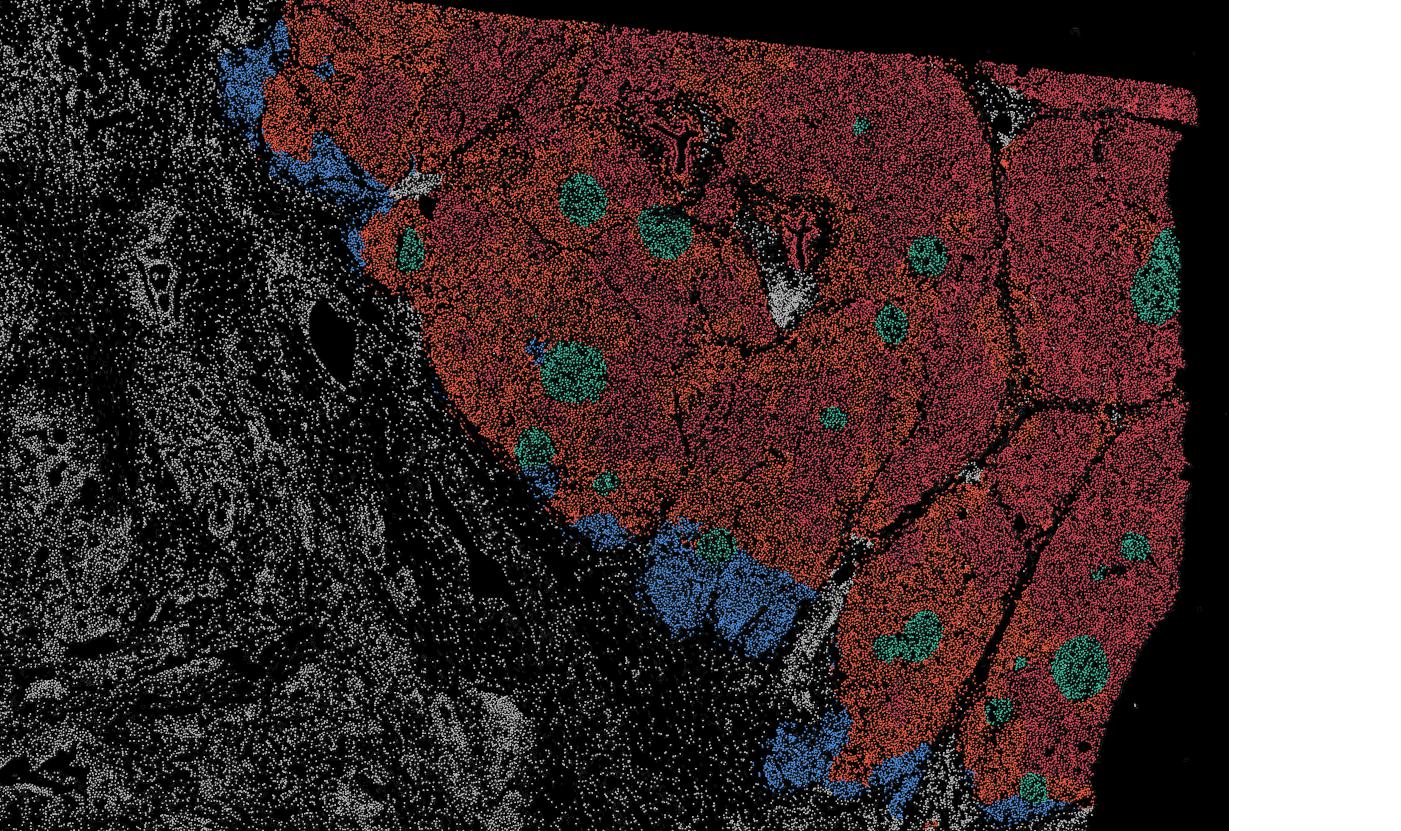
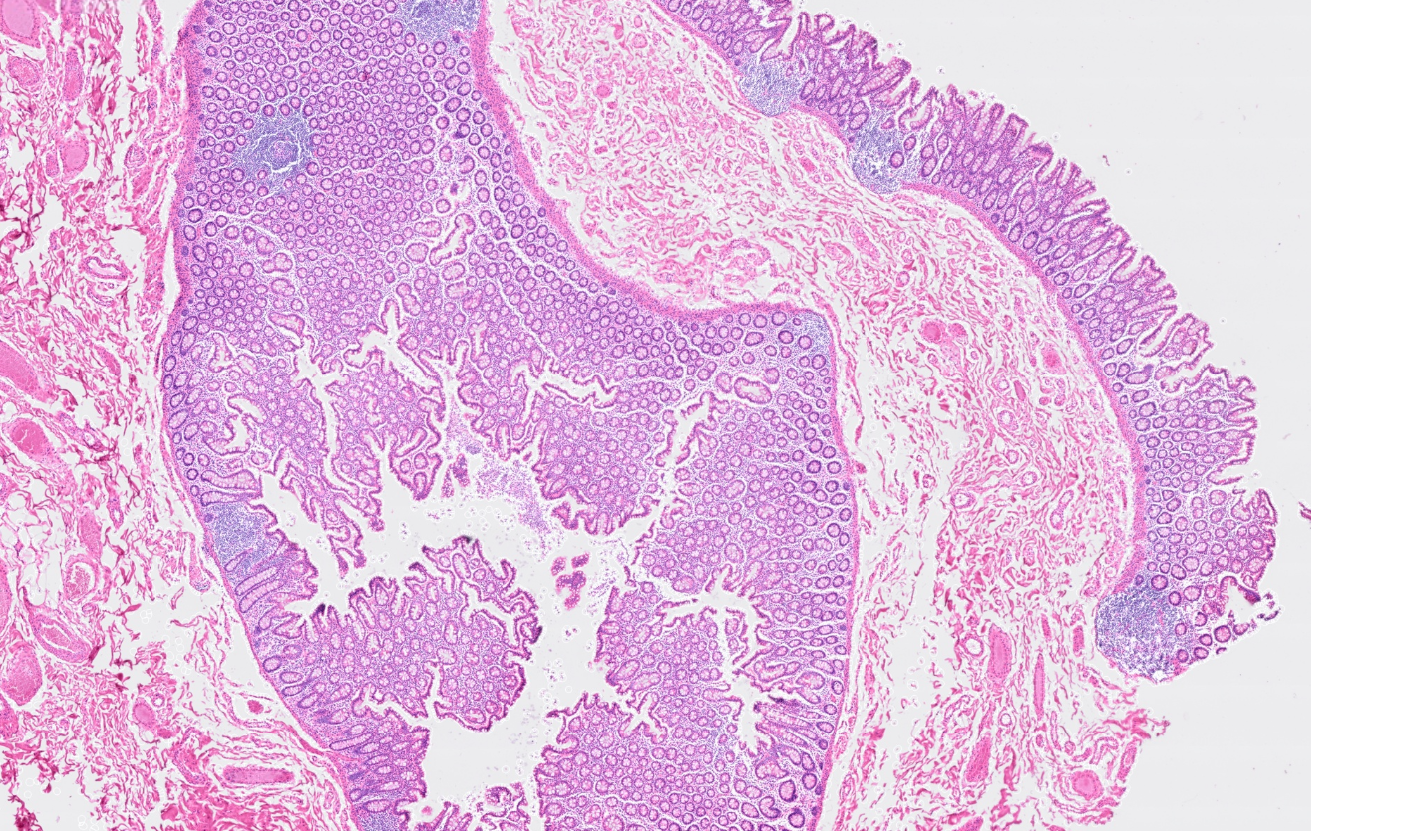
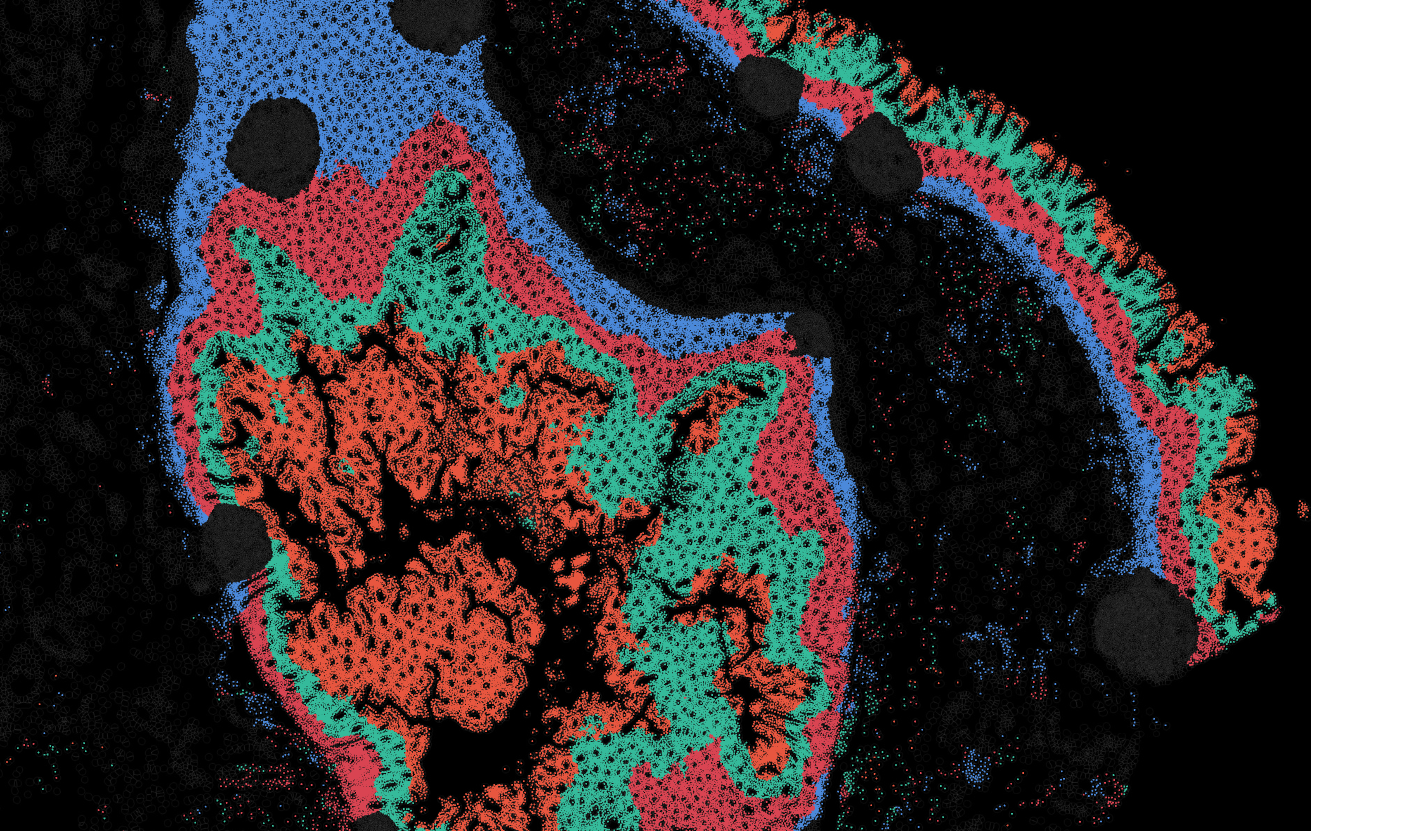
The segmentation module is designed to generalize across a wide range of biological tissues. Below are representative benchmark results based on 10x Genomics demo datasets:
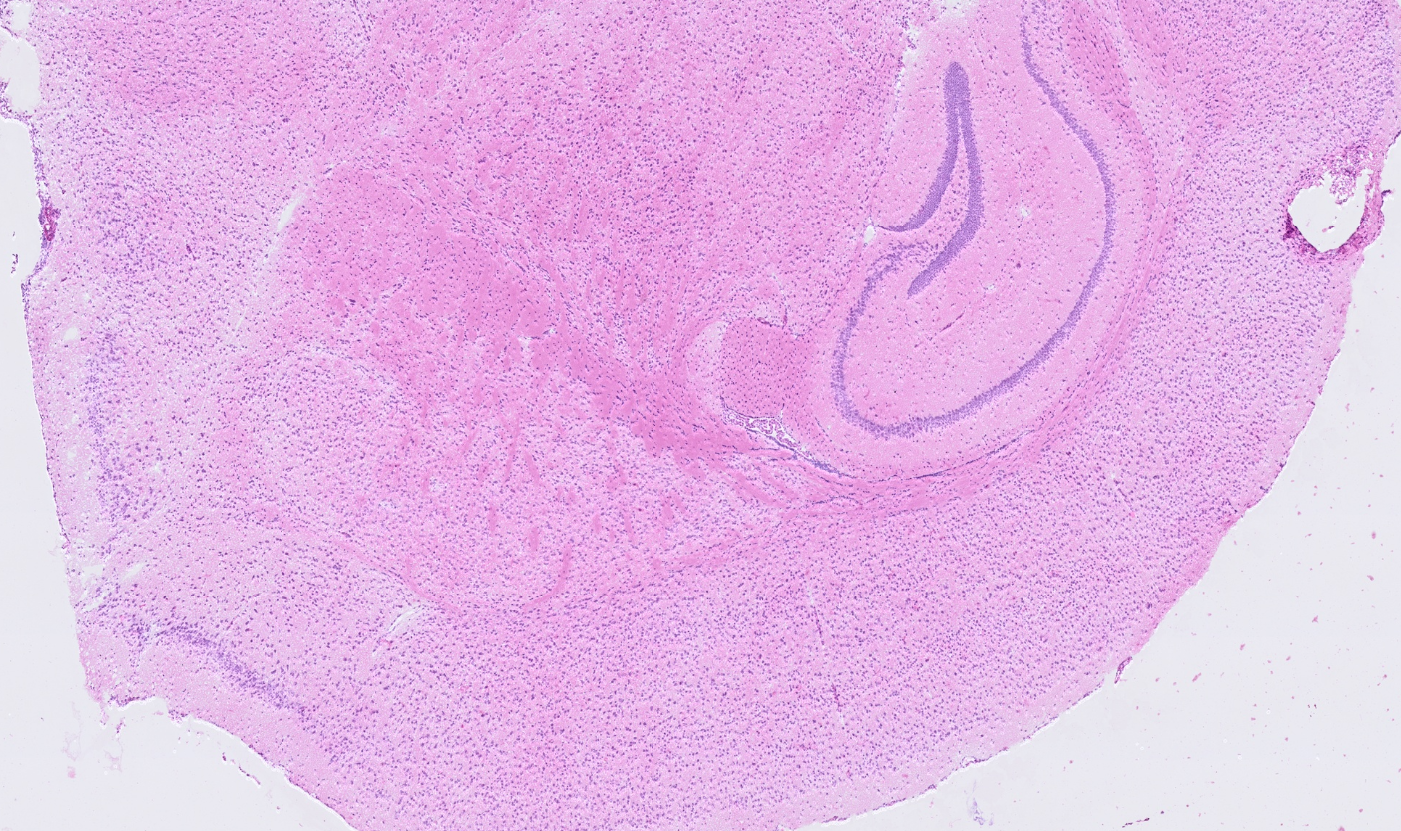
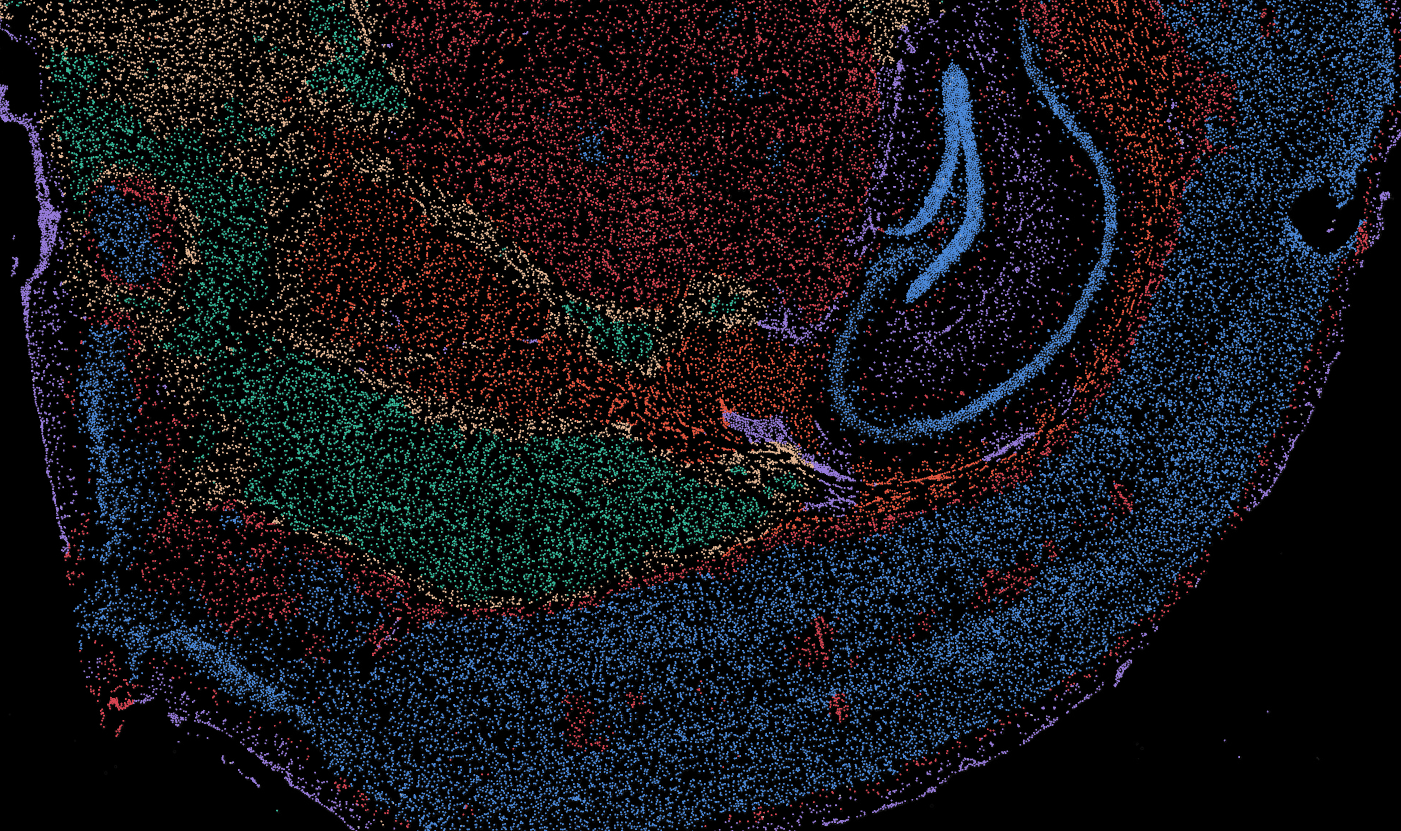
Brain
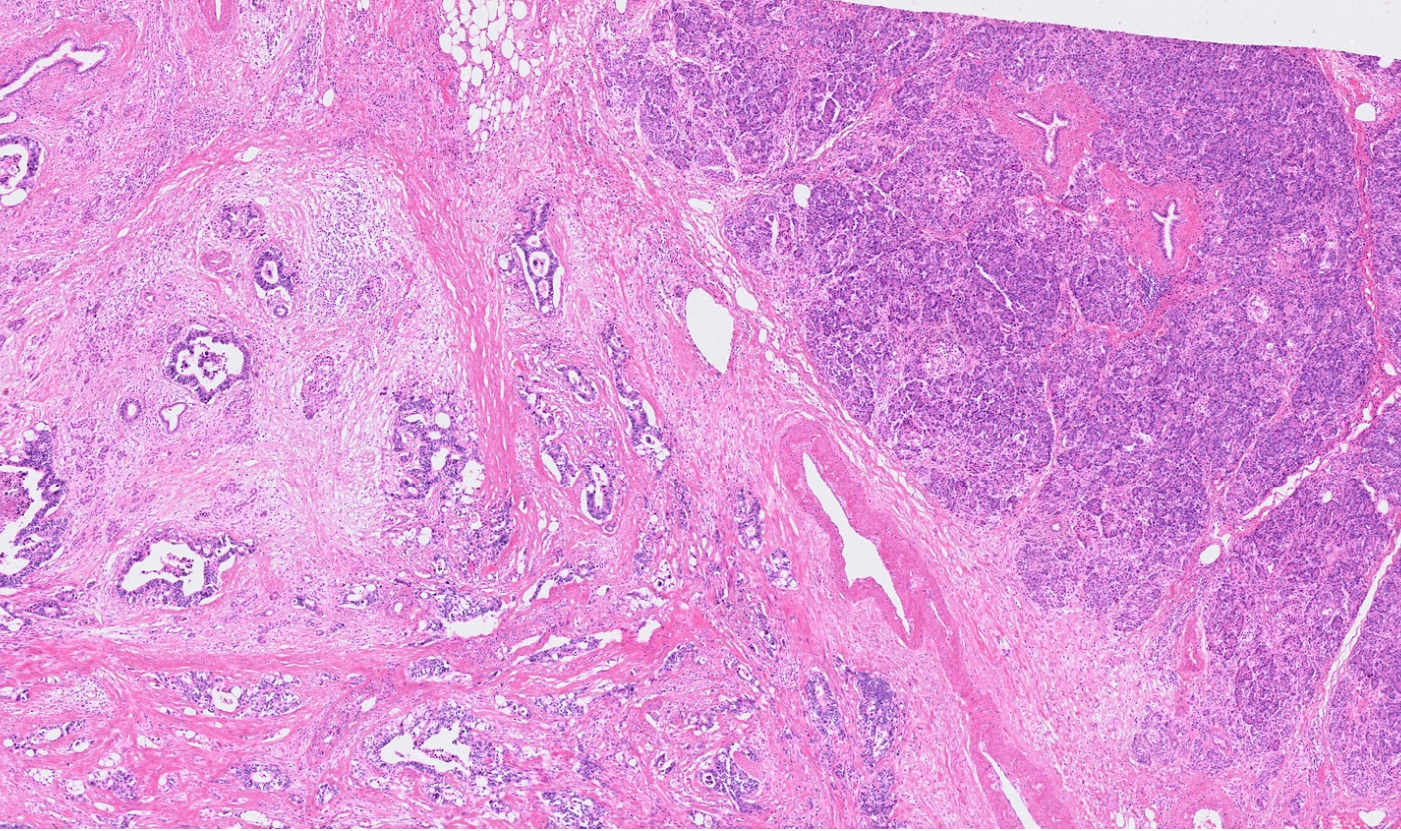
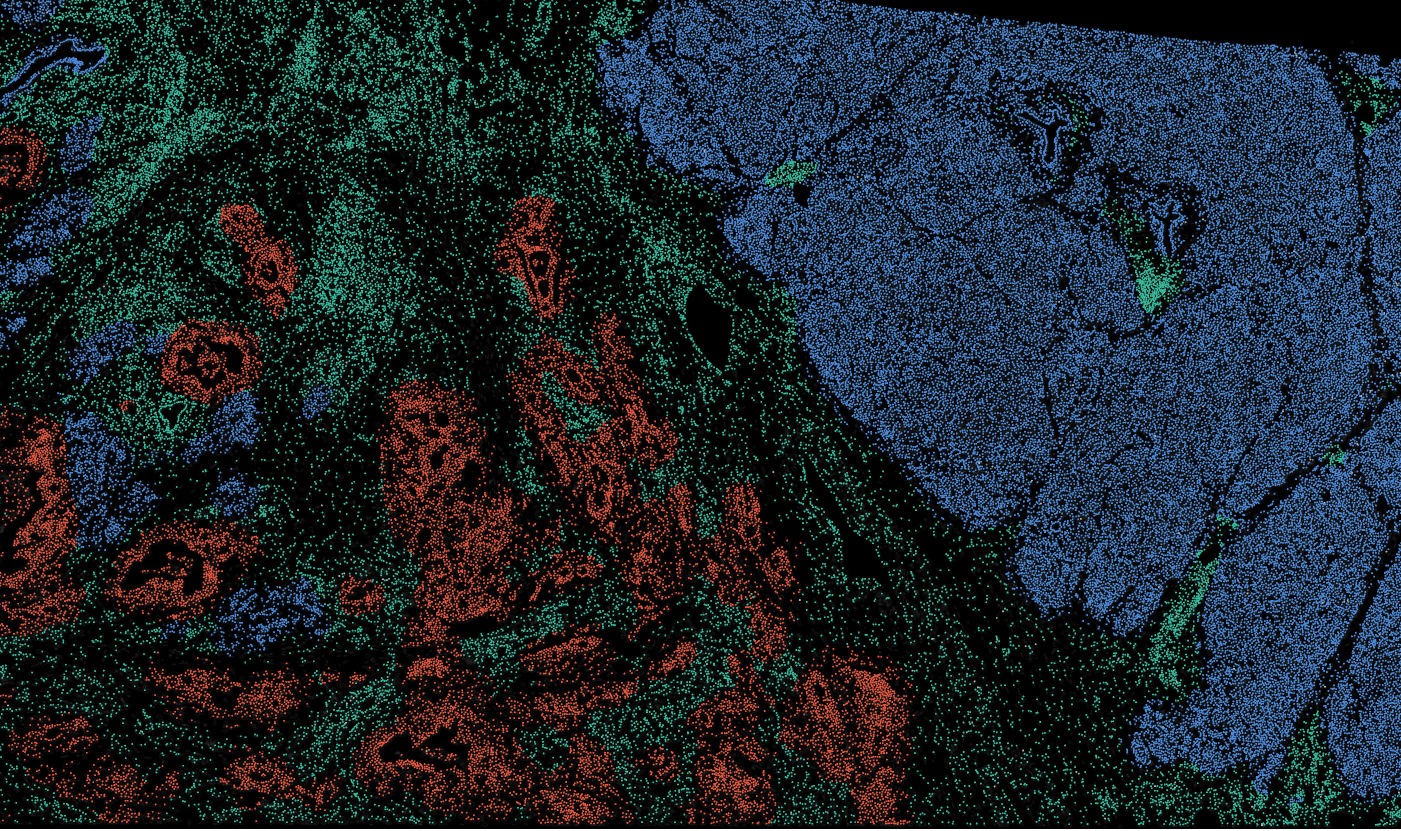
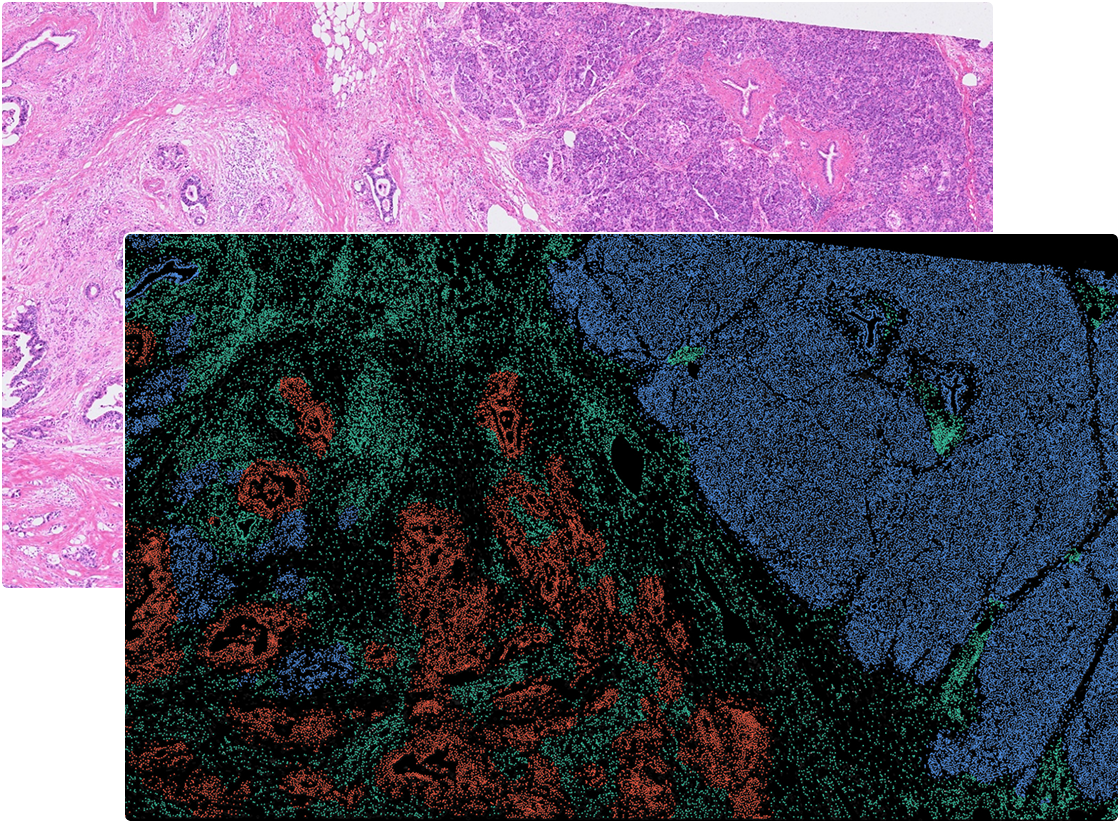
Pancreas
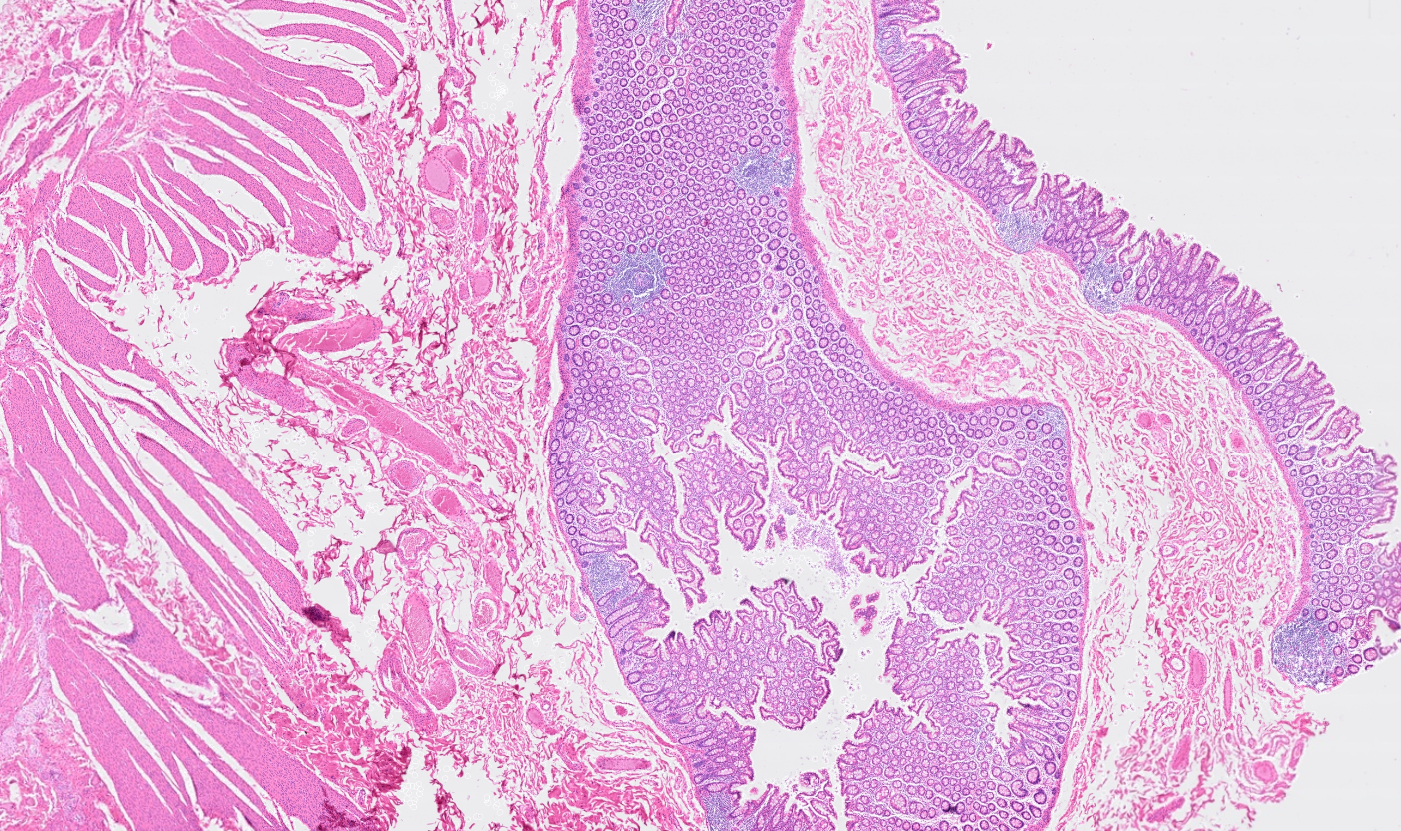
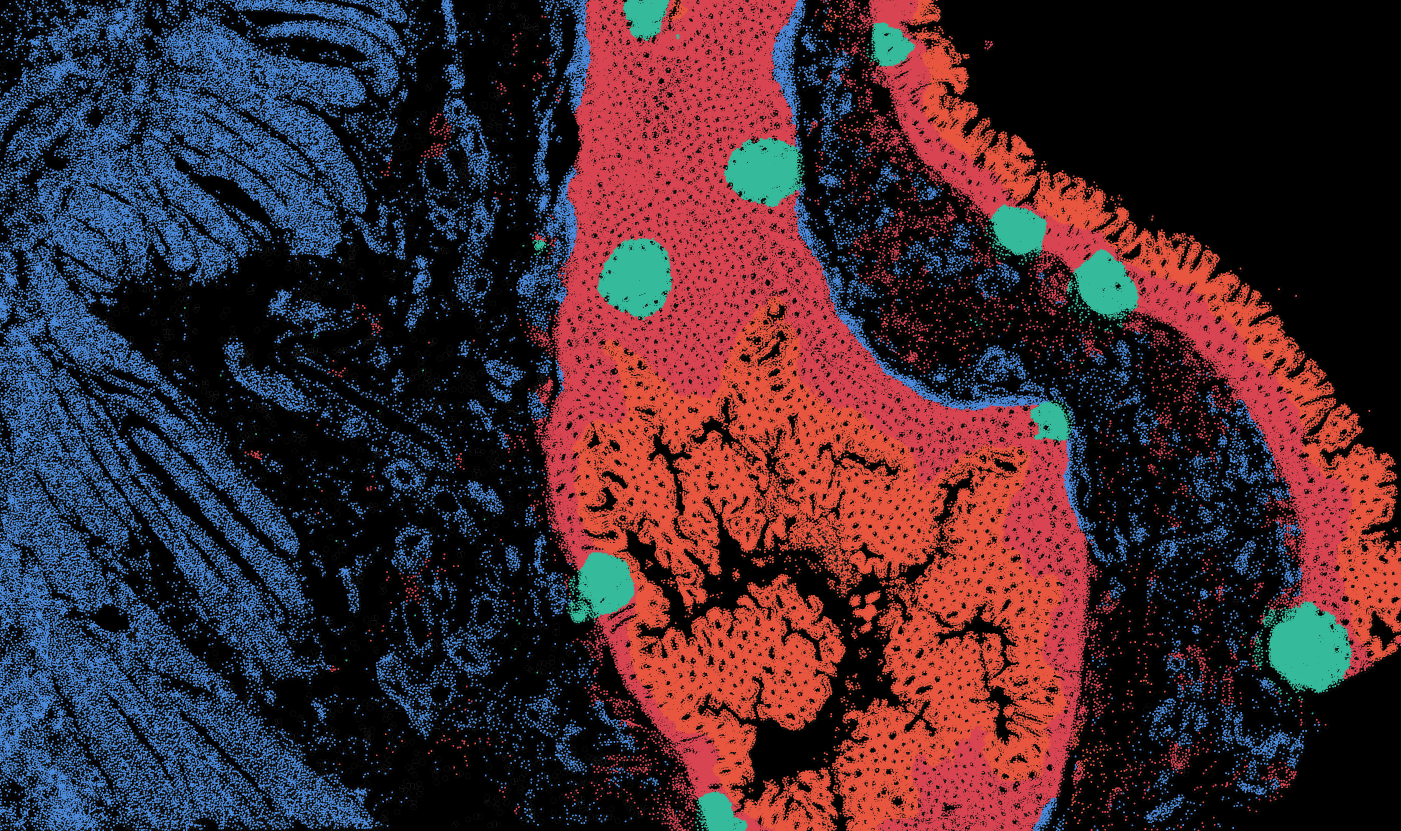
Colon
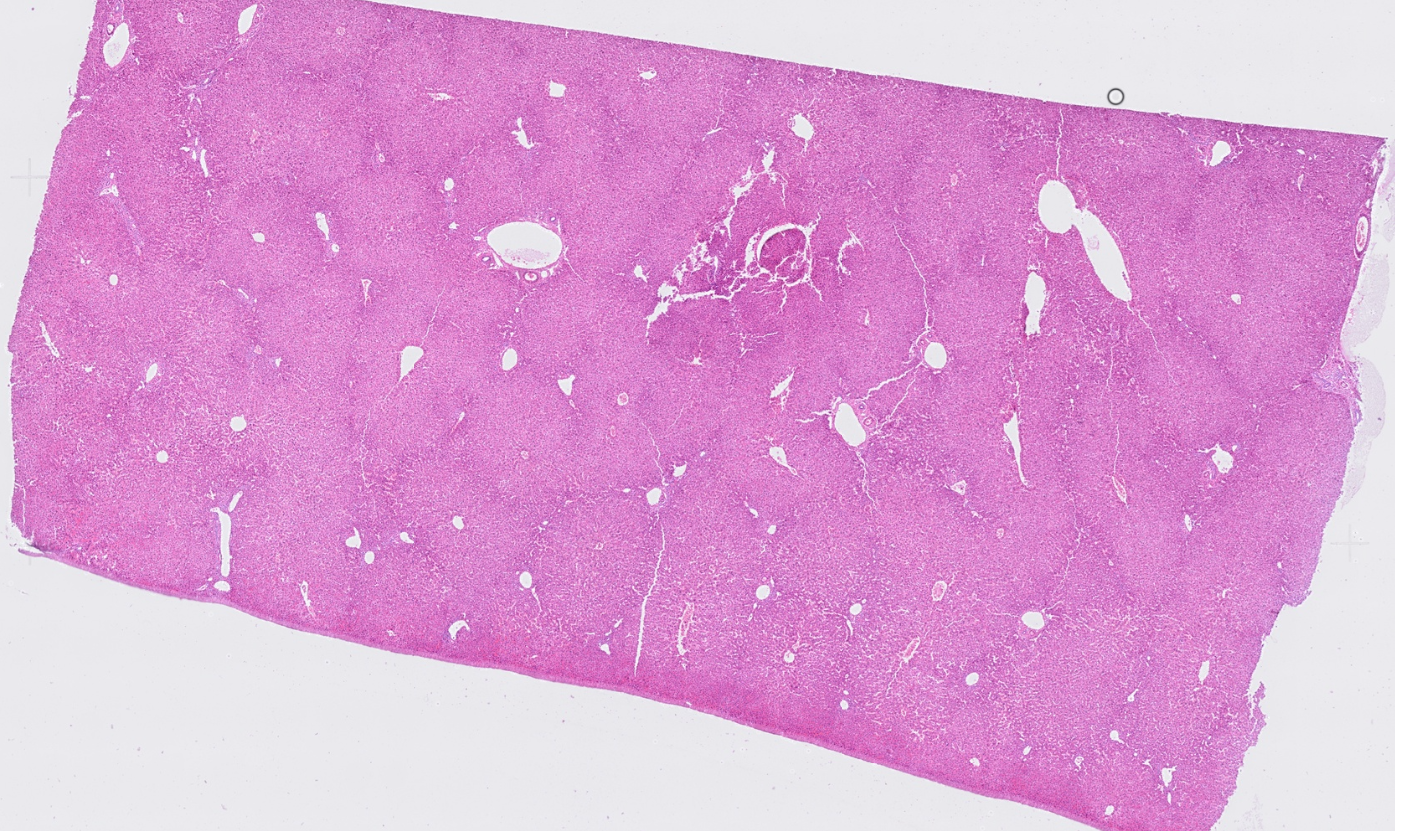
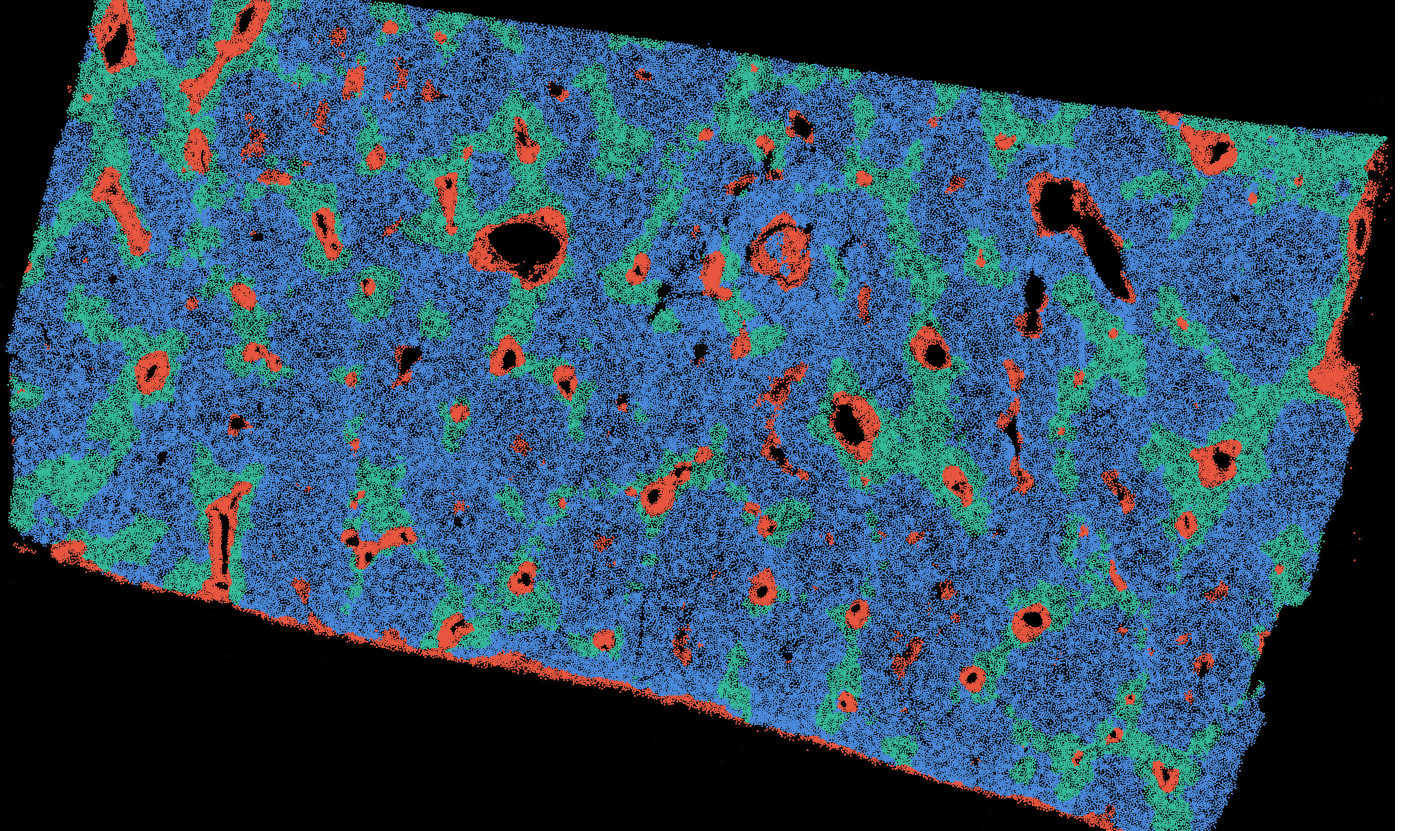
Liver
Ovary
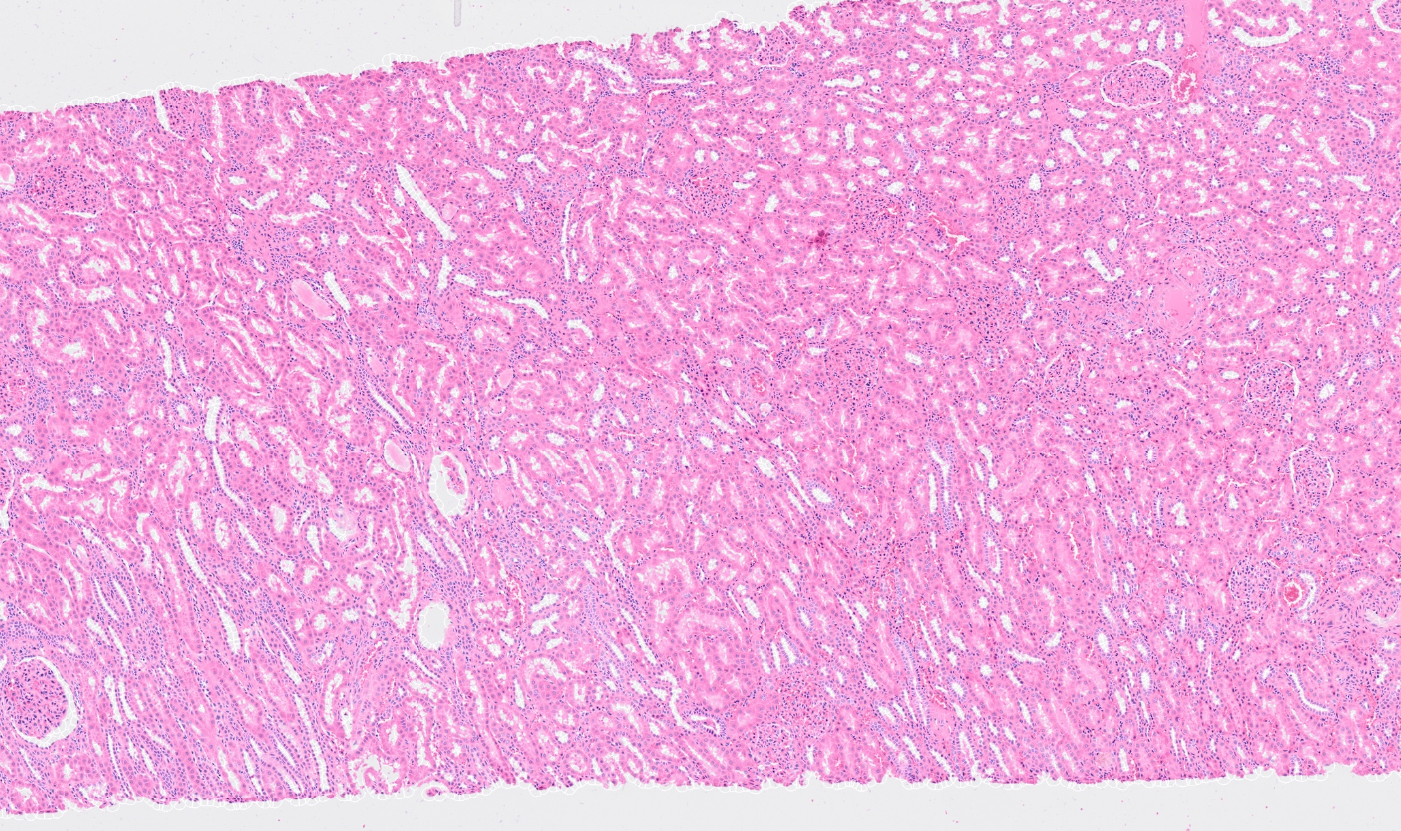
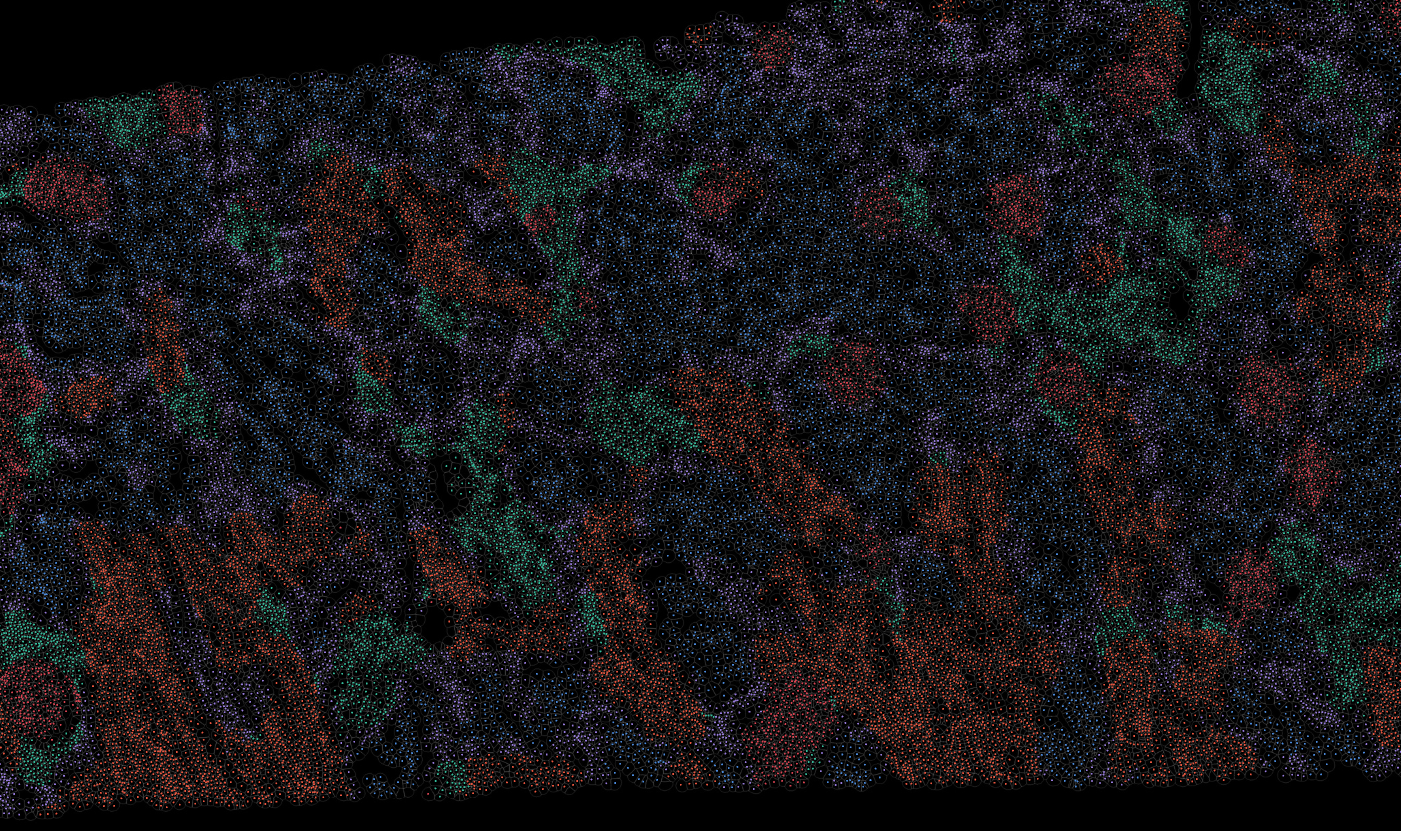
Kidney
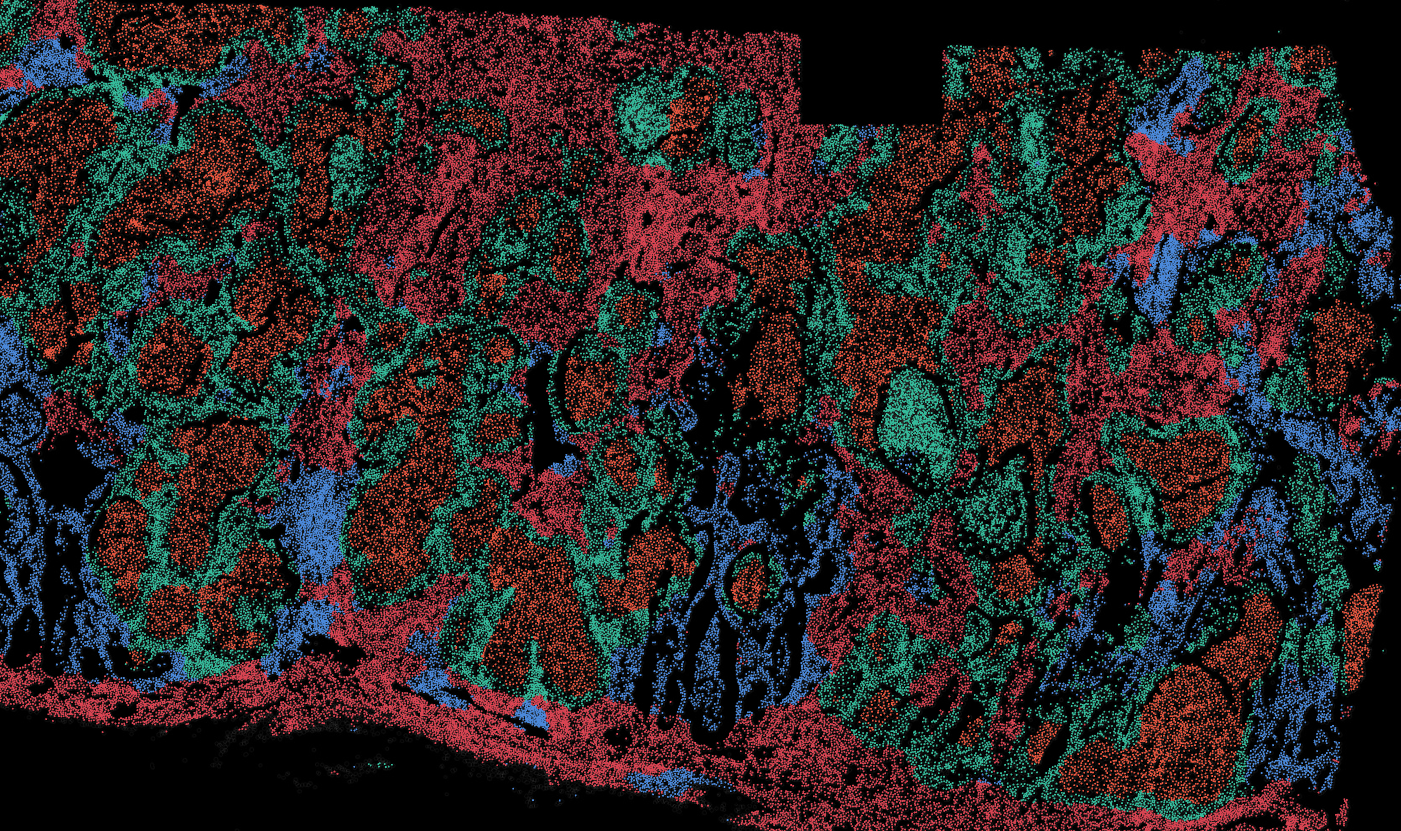
Lung
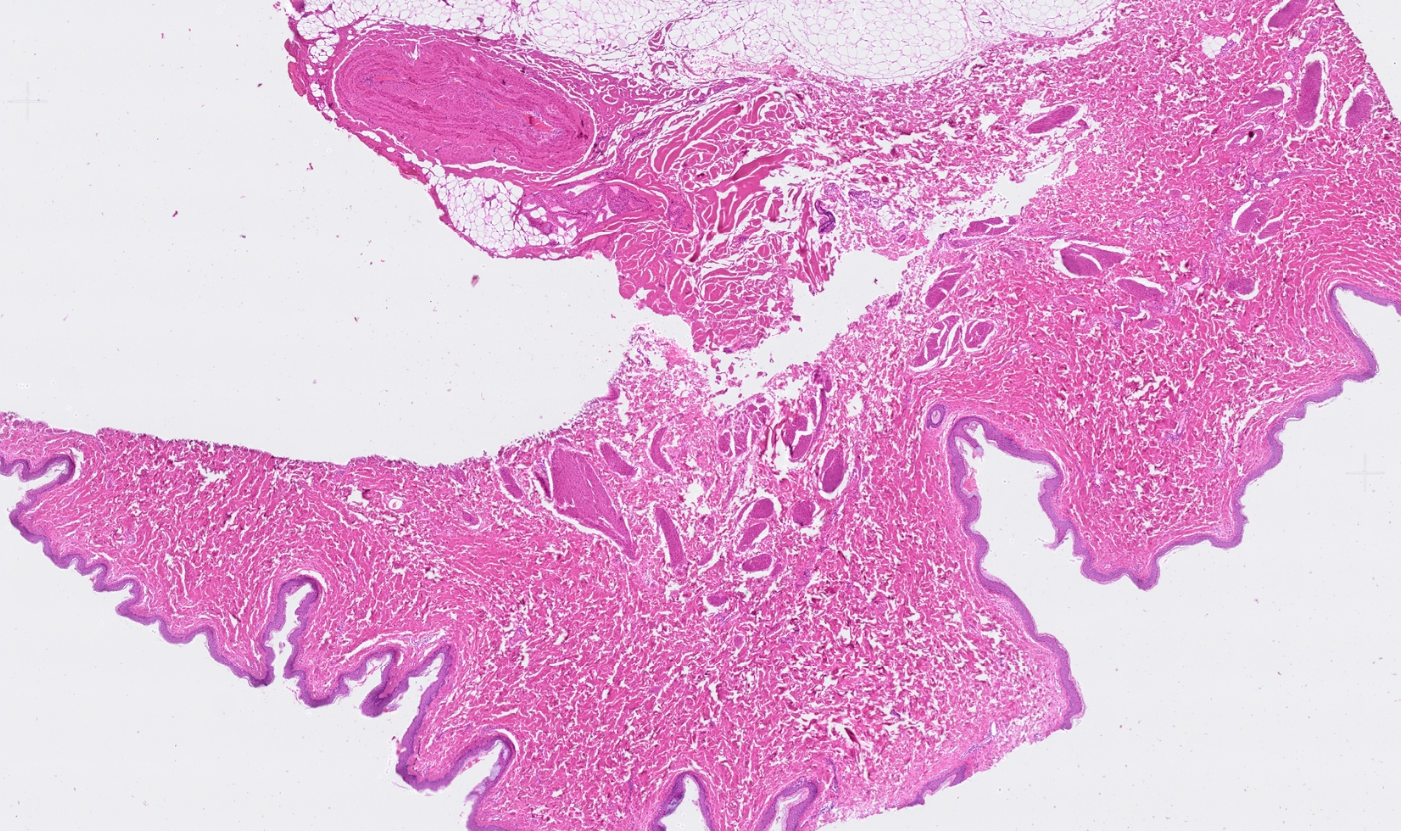
Skin
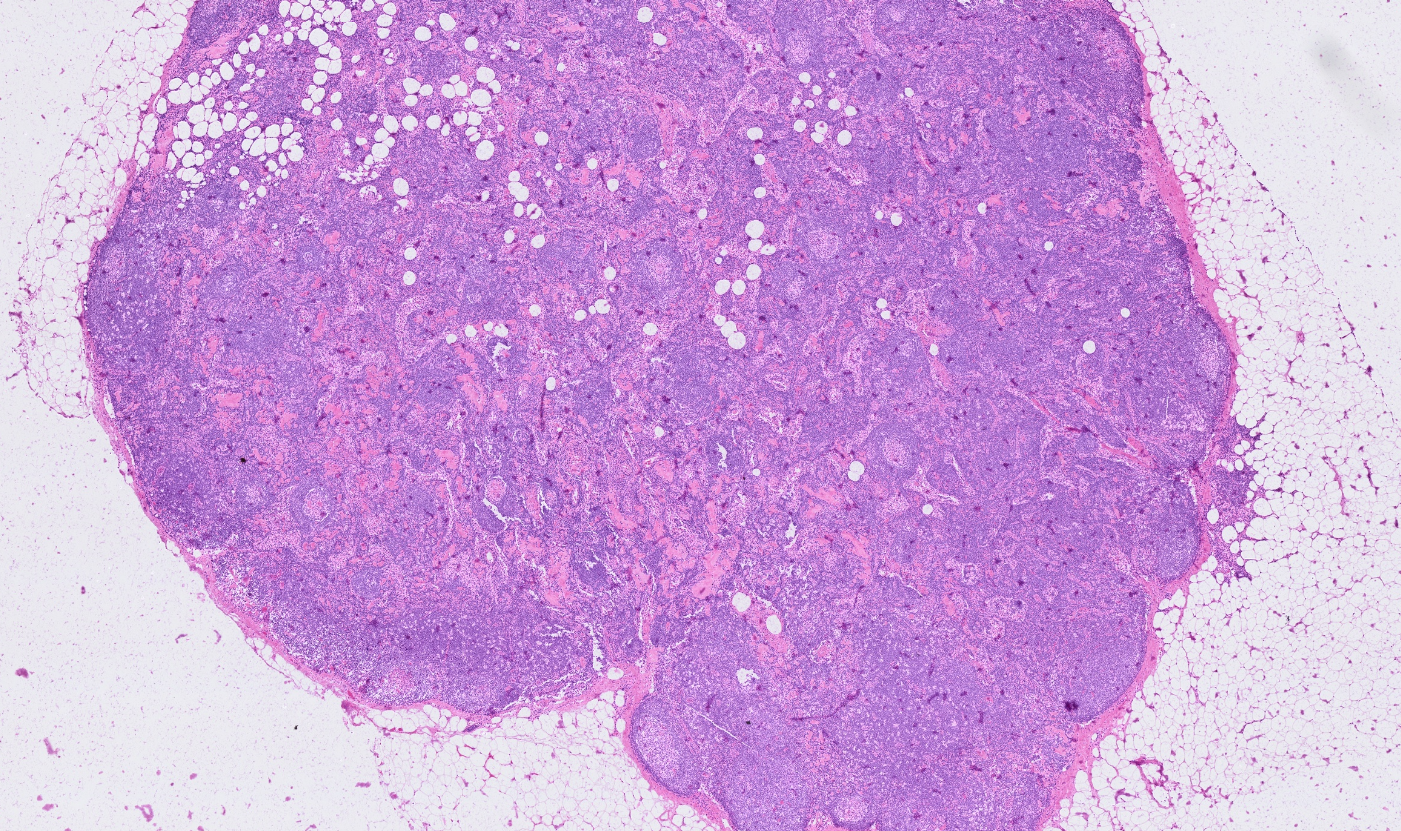
Lymph node
Applicability across different spatial resolutions
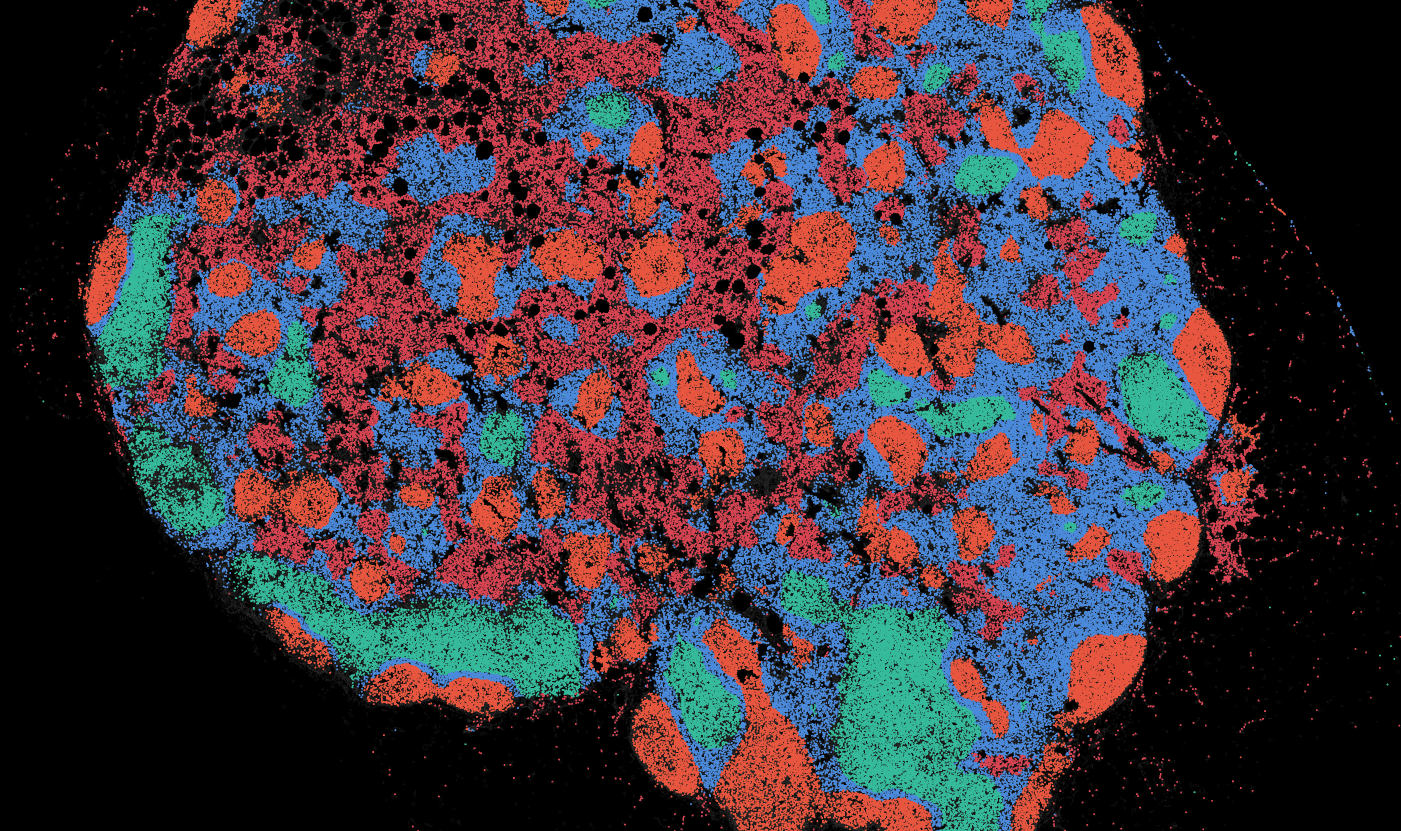
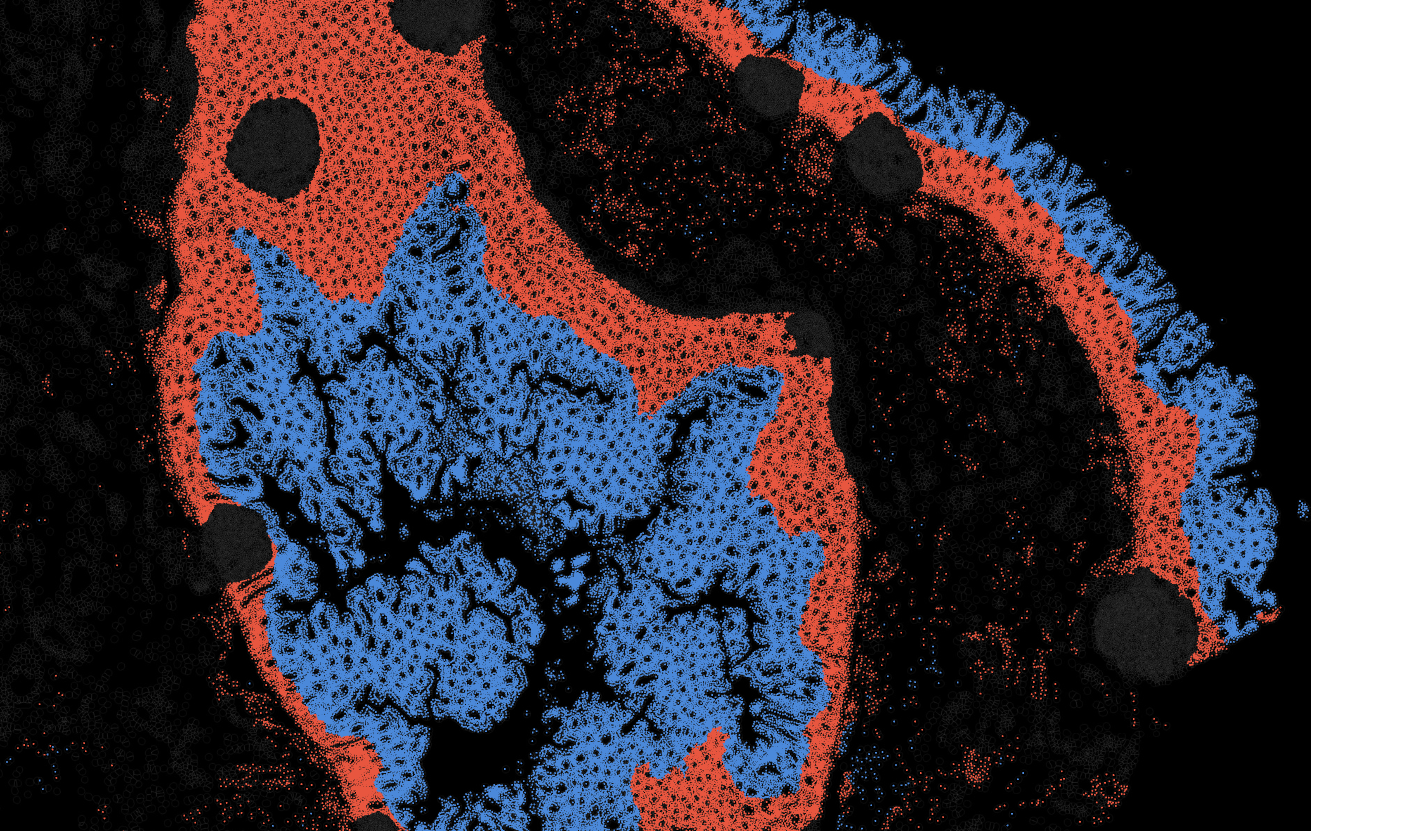
The segmentation module is designed to help researchers explore tissue architecture at multiple levels of detail, depending on their scientific question. Users can begin by dividing the tissue into major anatomical structures to gain a broad overview of the spatial landscape. From there, they can zoom into a specific region of interest and further segment it into sub-tissue compartments, enabling more refined analysis of microenvironments and localized biological processes.
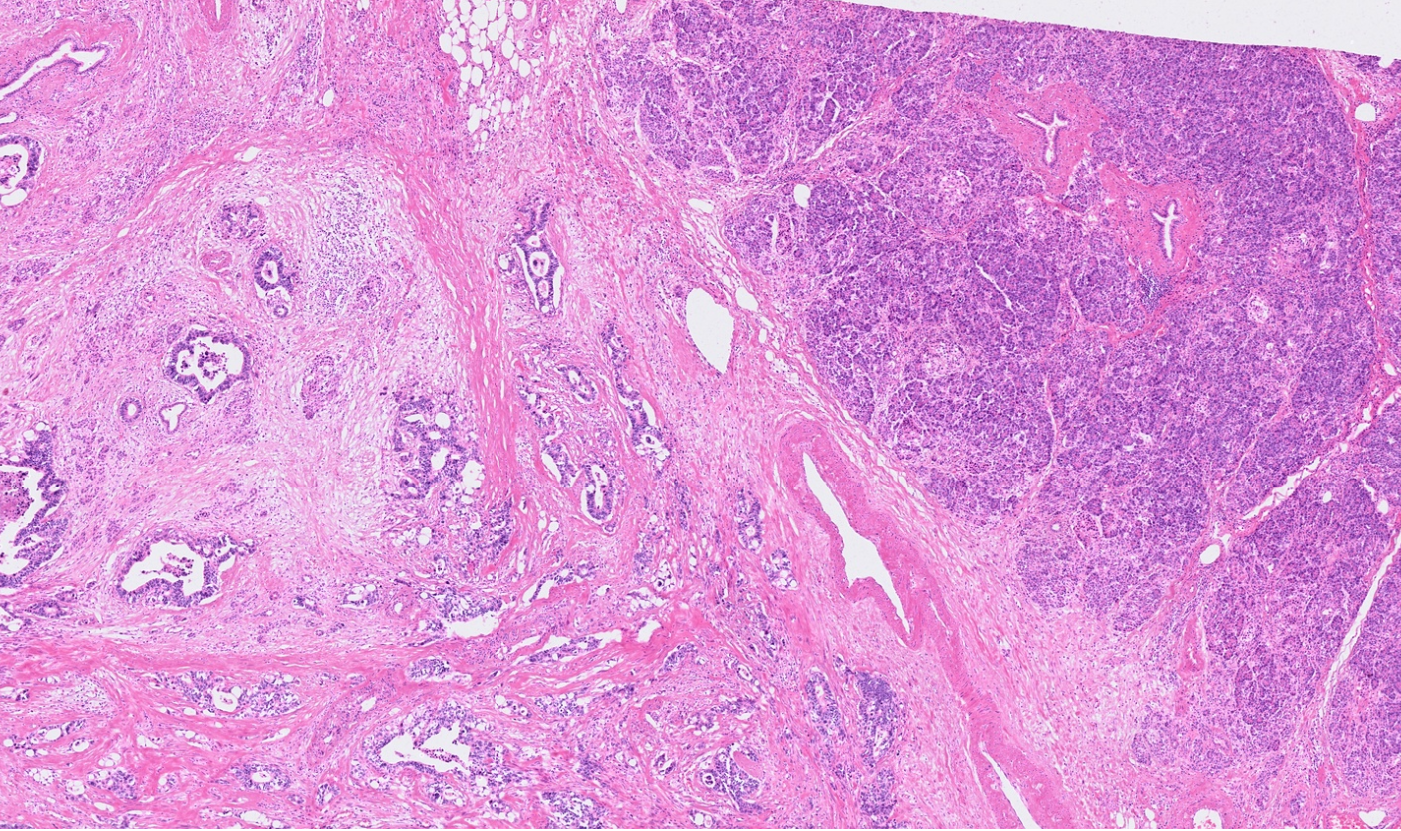
Streamline multi-omics data collaboration
OmnibusX brings research teams even closer together. Pathologists can now seamlessly annotate tissue images, providing critical insights that drive deeper biological analysis for every team member.
Experience the on your own data with a 2-month free trial at: https://omnibusx.com/apps. For questions, demo requests, or enterprise inquiries, feel free to contact us at: support@omnibusx.com
